PRODUCT
Material: Carbon steel
Finish:blue-white zinc plated
MOQ:1000PCS
Samples: Free
Standard:Non-standard , drawing or samples
Product Details
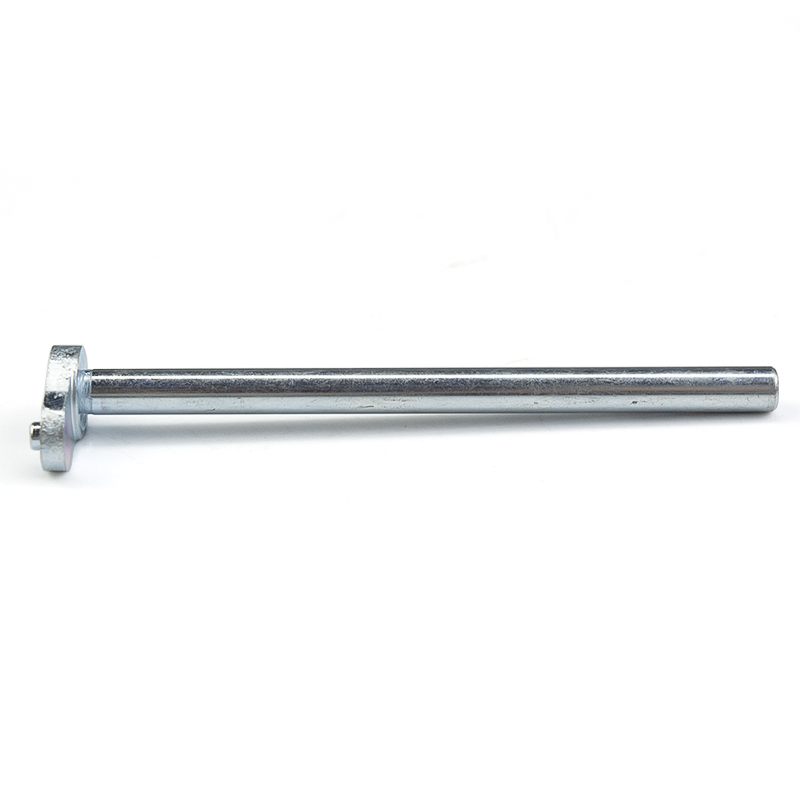
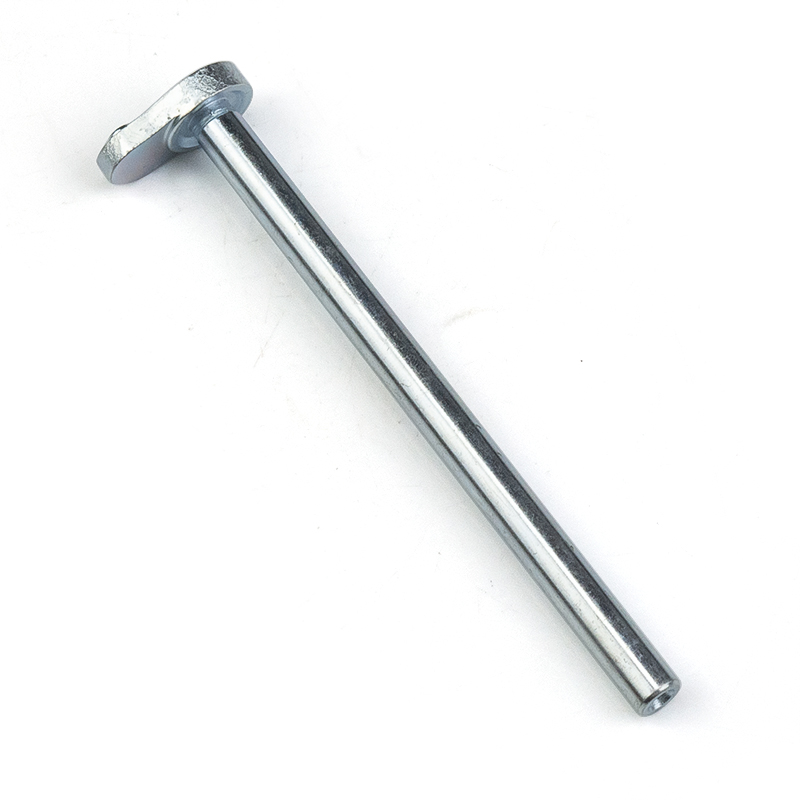
This is a custom-made double-hole ear-shaped connecting rod end head. It is made of high-quality carbon steel through hot forging and precise machining, and its surface is treated with environmentally friendly blue-white galvanization. The product structure consists of a long cylindrical smooth shaft body and the double-ear connection head at the end. The ear pieces are equipped with two different-sized holes: the large hole is an internal threaded through hole for main force connection; the small hole is a smooth through hole for auxiliary positioning or safety pin fixation. This "shaft body + double ears + double holes" integrated design enables it to be used as a pull rod, support rod or connection bridge in mechanical transmission systems, achieving long-distance force transmission and angle adaptation between components, and is widely applied in construction machinery, agricultural equipment, logistics handling, vehicle chassis and other fields. The non-standard customization feature allows for flexible adjustment of the shaft length, diameter thickness and ear hole layout, meeting the full range of transmission requirements from lightweight mechanisms to heavy equipment.
Long shaft body design
The middle section consists of straight rods of uniform diameter or stepped variable diameter, with the length customizable from 100 millimeters to 1000 millimeters. The surface is finely machined or polished, and can be used as the guide rail for sliding bearings or as a bridging shaft passing through multiple support plates.
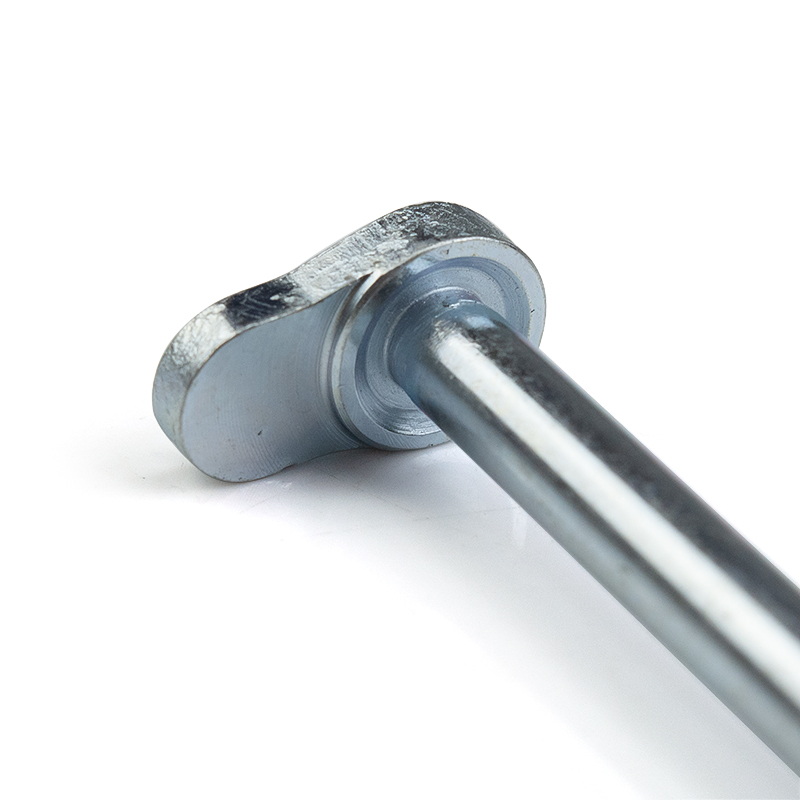
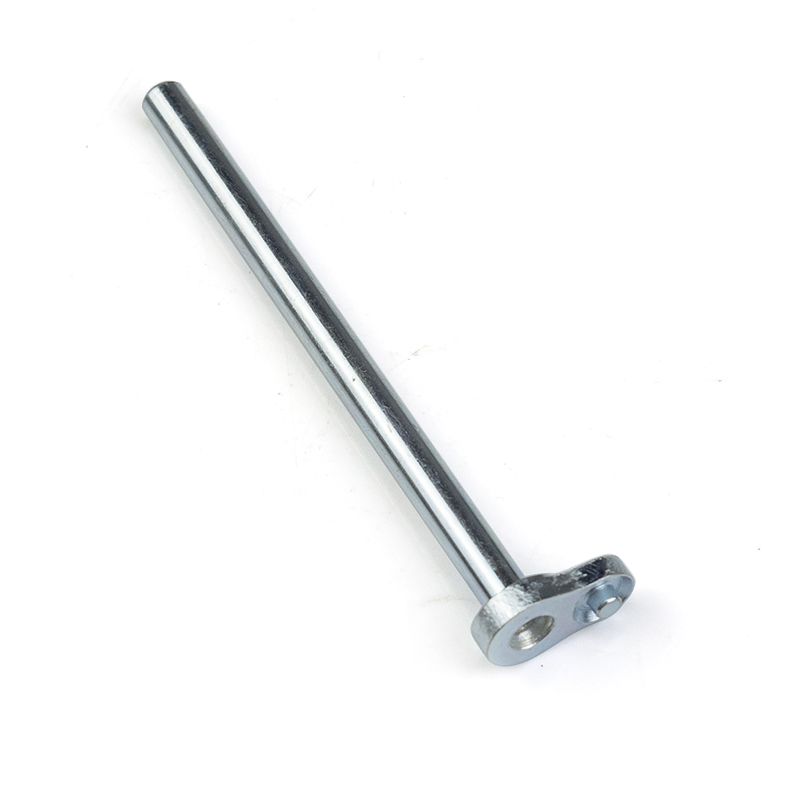
Double lug connection head
The end is forged into a flat double lug structure, with sufficient lug thickness to form a U-shaped joint for easy insertion and connection with the mating part's protruding lug. It is hinged through a pin shaft or bolt, allowing for a certain degree of swing and rotational freedom.
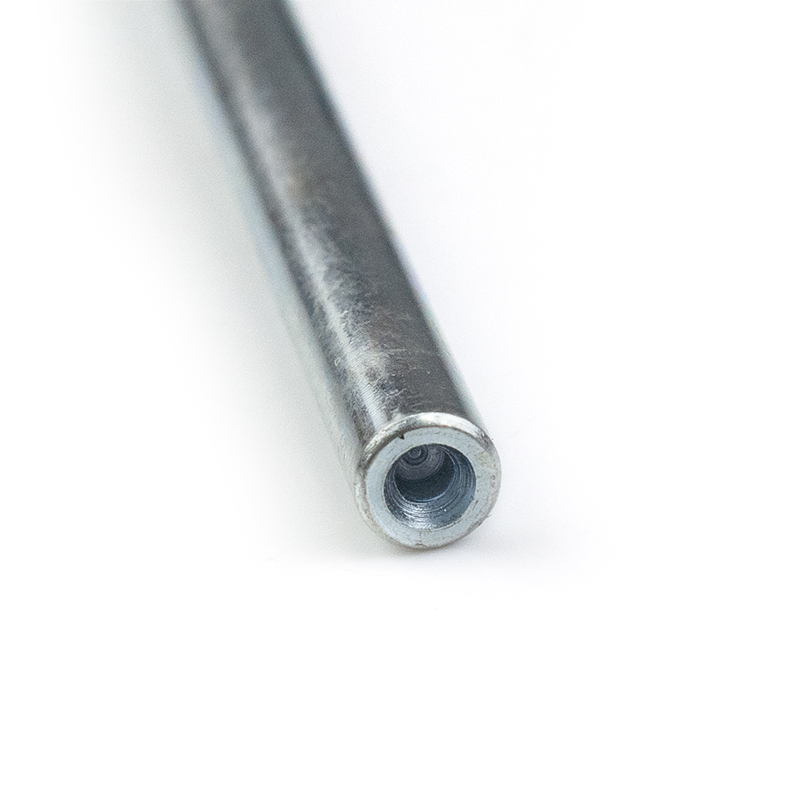
Primary and secondary double-hole configuration
The large hole is usually an M8 to M20 internal thread, bearing the main tension and compression loads; the small hole is a plain hole or shallow thread, used to pass safety pins to prevent loosening, or as an auxiliary lifting point or sensor installation position.
Forged strengthening
The junction between the lug and the shaft body is formed by hot forging as one piece, with a continuous metal flow line without any break, a full transitional arc, and significantly higher fatigue strength than welding or machined assembly structures.
Galvanization anti-corrosion protection
The surface is treated with blue-white galvanization, and undergoes a salt spray test for more than 48 hours, adapting to outdoor humid and dusty environments. The white passivation film facilitates visual inspection and maintenance status.
Direct force transmission path
The double-ear hinged structure enables the tension and compression loads to be directly transmitted along the axis of the rod body, without generating bending moments. The structure is highly efficient, and under the same cross-sectional area, the load-bearing capacity is improved by more than 30% compared to single-ear or bent plate structures.
Installation and adjustment are convenient
The internal threaded large hole allows the overall length to be adjusted by rotating the rod body, enabling continuous adjustment of the tension of the mechanism without the need to add or remove washers or replace parts. The maintenance and adjustment time is shortened by 80%.
Double safety anti-loosening
After the threaded connection, an open pin or R-shaped pin is inserted into the small hole to form mechanical anti-loosening. Even if the thread loosens, it cannot completely come off, meeting the safety standards for high-risk scenarios such as mines and high altitudes.
High space utilization
The slender rod body can span obstacles or pass through narrow spaces to connect distant components. The double-ear socket design allows the thickness of the mating parts to be unrestricted, and the layout flexibility far exceeds that of plate-type supports.
Long fatigue life
The forged streamline is distributed along the contour, and the arc transition at the root of the ear eliminates stress concentration. The hydrogen embrittlement control of the galvanized layer ensures a service life of up to 3 to 5 times that of welded structures under alternating loads.
Construction machinery chassis
The pusher rods of excavators and loaders, the boom support rods, and the steering rods, which bear intense vibrations and impacts, have double-ear hinging to adapt to terrain fluctuations.
Agricultural machinery equipment
The connecting rods of the suspension system of tractors, the parallel rods of the seeders, and the support rods of the harvesters, which can be adjusted in length to adapt to different crop row spacings.
Logistics handling equipment
The connecting rods of the mast tilting cylinders of forklifts, the connecting rods of the telescopic platforms, and the tension adjustment rods of the conveyor belts, which are lightweight and designed to reduce energy consumption.
Special vehicle modification
The leveling pull rods of the support legs of recreational vehicles, the connecting bridges of the support arms of rescue vehicles, and the auxiliary support rods of fire engine ladders, which have a double-safety design to ensure personnel safety.
Ship deck machinery
The opening and closing pull rods of hatch covers, the support rods for the gangways, and the fixing and binding rods for lifeboats, which have a corrosion-resistant version available in stainless steel.
Safety of amusement facilities
The connecting rods of the car body of roller coasters, the suspension arms of the cabins of Ferris wheels, and the pull rods of the large swing pendulums, which are forged to meet the safety certification requirements for special equipment.